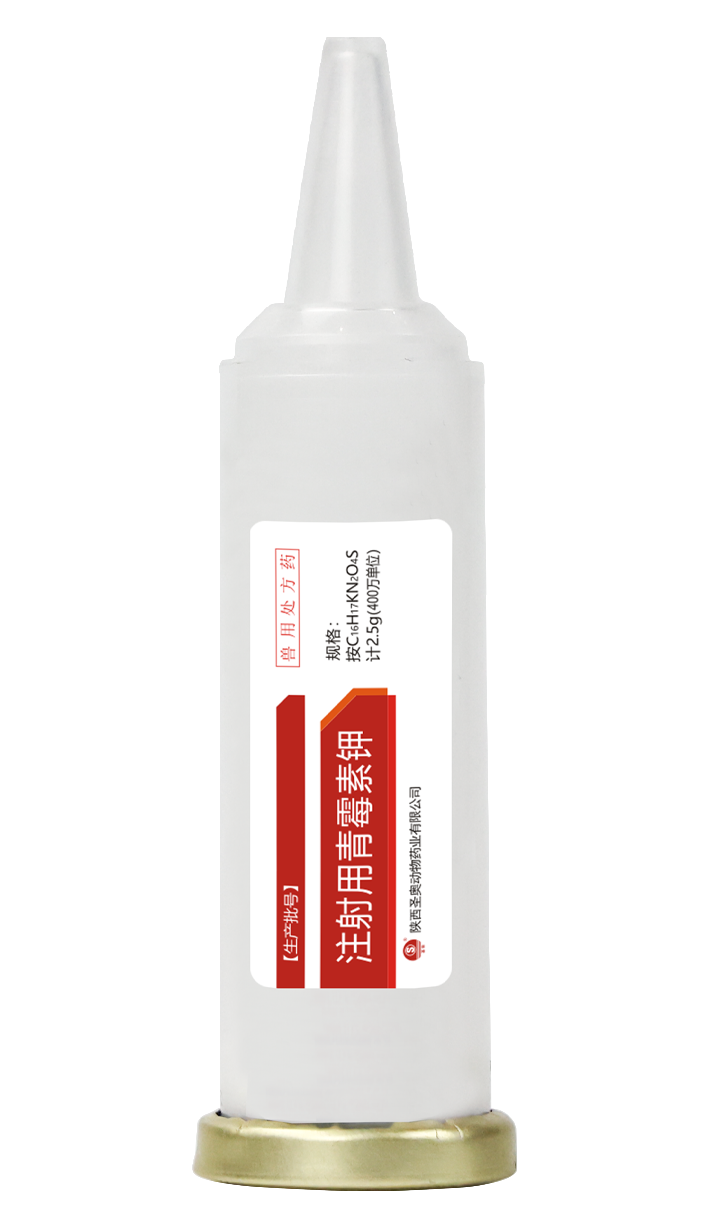
Penicillin Potassium for Injection
Key words:
Classification:
Detailed Description
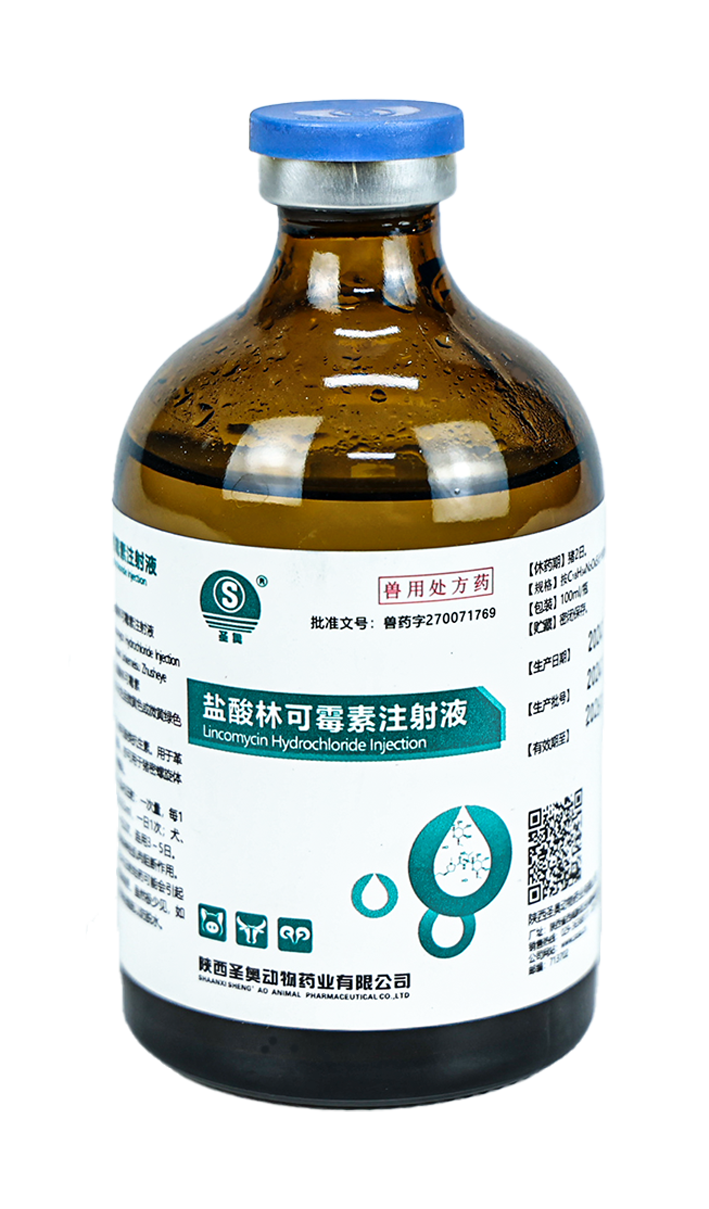
【Main components】Potassium penicillin
【Appearance】This product is a white crystalline powder.
【Pharmacological effects】Pharmacodynamics Penicillin is a bactericidal antibiotic with strong antibacterial activity. Its mechanism of antibacterial action is mainly to inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell wall mucopeptide. Sensitive bacteria in the growth phase are actively dividing, and the cell wall is in the biosynthesis phase. Under the action of penicillin, the synthesis of mucopeptide is inhibited, and the cell wall cannot be formed, leading to cell membrane rupture and death under osmotic pressure. In non-growing and non-reproducing bacteria, there is no need to synthesize the cell wall at this time, so penicillin does not have a bactericidal effect. Penicillin, a "growth-phase bactericide", should not be used in combination with "rapidly acting bacteriostatic agents" (such as florfenicol, tetracyclines, erythromycin, etc.) that inhibit bacterial growth and reproduction. The latter puts bacteria in a growth-inhibited state, preventing penicillin from working.
Penicillin is a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, mainly effective against various Gram-positive bacteria and a few Gram-negative bacteria. The main sensitive bacteria include Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, Corynebacterium, Clostridium tetani, Actinomyces, Bacillus anthracis, and spirochetes. It is not sensitive to mycobacteria, mycoplasma, chlamydia, rickettsia, Nocardia, fungi, and viruses.
Pharmacokinetics After intramuscular injection of potassium penicillin salt, it is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak blood concentration in 15-30 minutes. The blood concentration after intramuscular injection is maintained above 0.5 μg/ml for 6-7 hours. Penicillin is widely distributed to various tissues throughout the body and can enter the fetal circulation, with higher concentrations in the kidney, liver, lung, muscle, small intestine, and spleen; lower concentrations in bone, saliva, and milk. It is difficult to enter the cerebrospinal fluid, and its concentration in normal cerebrospinal fluid is only 1%-3% of the blood concentration; in inflammation, the concentration in cerebrospinal fluid can reach 5%-30% of the blood concentration. The concentration of penicillin in milk can be 5%-20% of the blood concentration. When penicillin is injected into the mammary gland, a large amount is absorbed in the first few hours, but the antibacterial concentration can be maintained in the milk for a considerable period of time. It has been reported that after injecting 100,000 units of penicillin aqueous solution into the mammary gland, it can remain at 4.26 units/ml in the milk for up to 24 hours.
A small portion of penicillin is metabolized in the liver, and most is excreted in its original form. Under normal renal function, 50%-75% is excreted by the kidneys, of which 90% is secreted by the renal tubules. Due to rapid excretion, it is eliminated from the body relatively quickly. The plasma protein binding rate of penicillin is about 50%. The half-life is short, and the interspecies differences are small, with a half-life of 0.5-1.2 hours for all livestock. The apparent volume of distribution is also small, generally 0.2-0.3 L/kg, with a high plasma concentration and a low tissue concentration.
【Drug interactions】(1) Combined use of penicillin and aminoglycosides can increase the concentration of the latter in the bacteria, showing a synergistic effect.
(2) Rapidly acting bacteriostatic agents such as macrolides, tetracyclines, and aminoglycosides interfere with the bactericidal activity of penicillin and should not be used together.
(3) Heavy metal ions (especially copper, zinc, mercury), alcohols, acids, iodine, oxidants, reductants, hydroxyl compounds, acidic glucose injection or tetracycline hydrochloride injection, etc., can destroy the activity of penicillin and are prohibited from being used together.
(4) Amines can form insoluble salts with penicillin, which can delay the absorption of penicillin, such as procaine penicillin.
(5) Potassium penicillin aqueous solution should not be mixed with some drug solutions (such as chlorpromazine hydrochloride, lincomycin hydrochloride, norepinephrine tartrate, oxytetracycline hydrochloride, tetracycline hydrochloride, B vitamins, and vitamin C), otherwise turbidity, flocculation, or precipitation may occur.
【Action and use】β-lactam antibiotics. Mainly used for Gram-positive bacterial infections, also used for infections caused by Actinomyces and Leptospira.
【Dosage and administration】Calculated as potassium penicillin. Intramuscular injection: Single dose, per 1 kg body weight, horses and cattle 10,000-20,000 units; sheep, pigs, foals, calves 20,000-30,000 units; poultry 50,000 units; dogs and cats 30,000-40,000 units. 2-3 times a day, for 2-3 days.
Dissolve with an appropriate amount of sterile water for injection before use.
【Adverse reactions】(1) Mainly allergic reactions, which can occur in most livestock, but the incidence is low. Local reactions manifest as edema and pain at the injection site, systemic reactions as urticaria and rash, and severe cases can cause shock or death.
(2) In some animals, penicillin can induce superinfection of the gastrointestinal tract.
【Precautions】(1) Poultry that lay eggs for human consumption should not be used during the egg-laying period.
(2) Potassium penicillin is easily soluble in water, but the aqueous solution is unstable and easily hydrolyzed. The hydrolysis rate accelerates with increasing temperature, so the injection should be prepared immediately before use. If it needs to be stored, it should be placed in a refrigerator (2-8℃) and can be stored for 7 days. At room temperature, it can only be stored for 24 hours.
(3) The interaction and contraindications with other drugs should be understood to avoid affecting the efficacy of penicillin.
(4) High doses may cause hyperkalemia. This can have adverse consequences for animals with impaired renal or cardiac function, and the adverse effects of potassium ions on the heart are more serious.
(5) When treating tetanus, it should be used in combination with tetanus antitoxin.
【Withdrawal period】Cattle, sheep, pigs, poultry 0 days; milk withdrawal period 72 hours.
【Specifications】Calculated as C16H17KN2O4S 2.5g (4 million units)
【Packaging】10 vials/box × 40 boxes/carton
【Storage】Sealed and stored in a cool, dark, and dry place.
【Shelf life】Two years
Related Products
Contact Information
Contact Address

Address: Jinghe Xincheng Jingyong Road Middle Industrial Park, Xixian New District, Shaanxi Province